vSAN-8 launched with a brand new storage architecture for vSAN called VMware vSAN Express Storage Architecture™ or ESA along side with a few enhancements to vSAN-OSA which is the Original Storage Architecture.
Users are given an option at the beginning of vSAN Cluster setup with vSphere-8 to choose either of the architecture, in this blog I explain what are the key features and enhancements of vSAN ESA and how it compares to OSA.
History of vSAN-OSA!
At the time of vSAN OSA launch back in the days during vSphere 5.5 we only had 1G/10G networks, SSDs were super expensive vs HDDs and CPU cores were very limited, hence this architecture primarily focused to cater a decent performance with available hardware during the time.
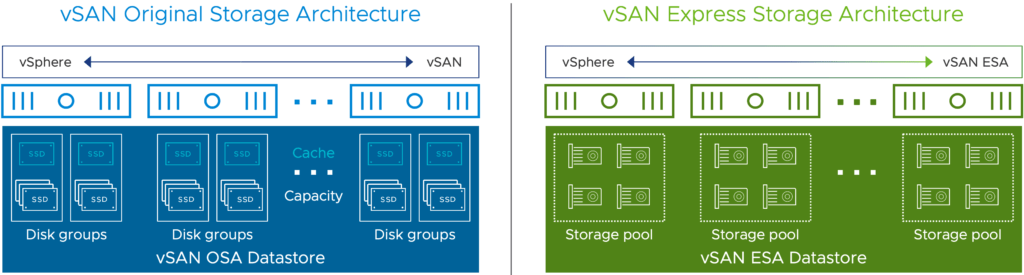
When new features were added to vSAN-OSA with vSphere 6.x release such as support for All-Flash Technology, Erasure coding (RAID-5 / RAID-6), Deduplication & Compression, encryption etc we started to see some tradeoffs in terms of performance when using one or more features and the performance penalty was a little bit higher when running a stretched cluster between two sites with these features. The total available raw capacity was also less because every diskgroup has to have a dedicated Cache disk which doesn’t contribute to over all raw usable capacity.
vSphere 7.x/vSAN 7.x brought in significant performance improvements when using Erasure Coding, Compression-Only feature,Data in Transit Encryption. These features did improve performance overall, however vSAN OSA could not scale very well due to inherent architectural limitations to exploit capabilities new generation storage devices (PMEM,OPTANE,MLC,TLC,QLC), new generation CPUs and faster network devices(25G,40G and 100G).
Having said that OSA will continue to stay in the market along with ESA, infact the 600Gb Write Buffer for cache disk is improved to 1.6Gb, I will talk about this on a separate article.
Why vSAN ESA?
vSAN-ESA is an alternative optimized architecture to exploit full potential of the very latest hardware (Storage/CPU/Network) to provide highly efficient, scalable, and performant HCI clusters by driving latencies for the modern application/workload lower and providing very high throughput and IOPS.
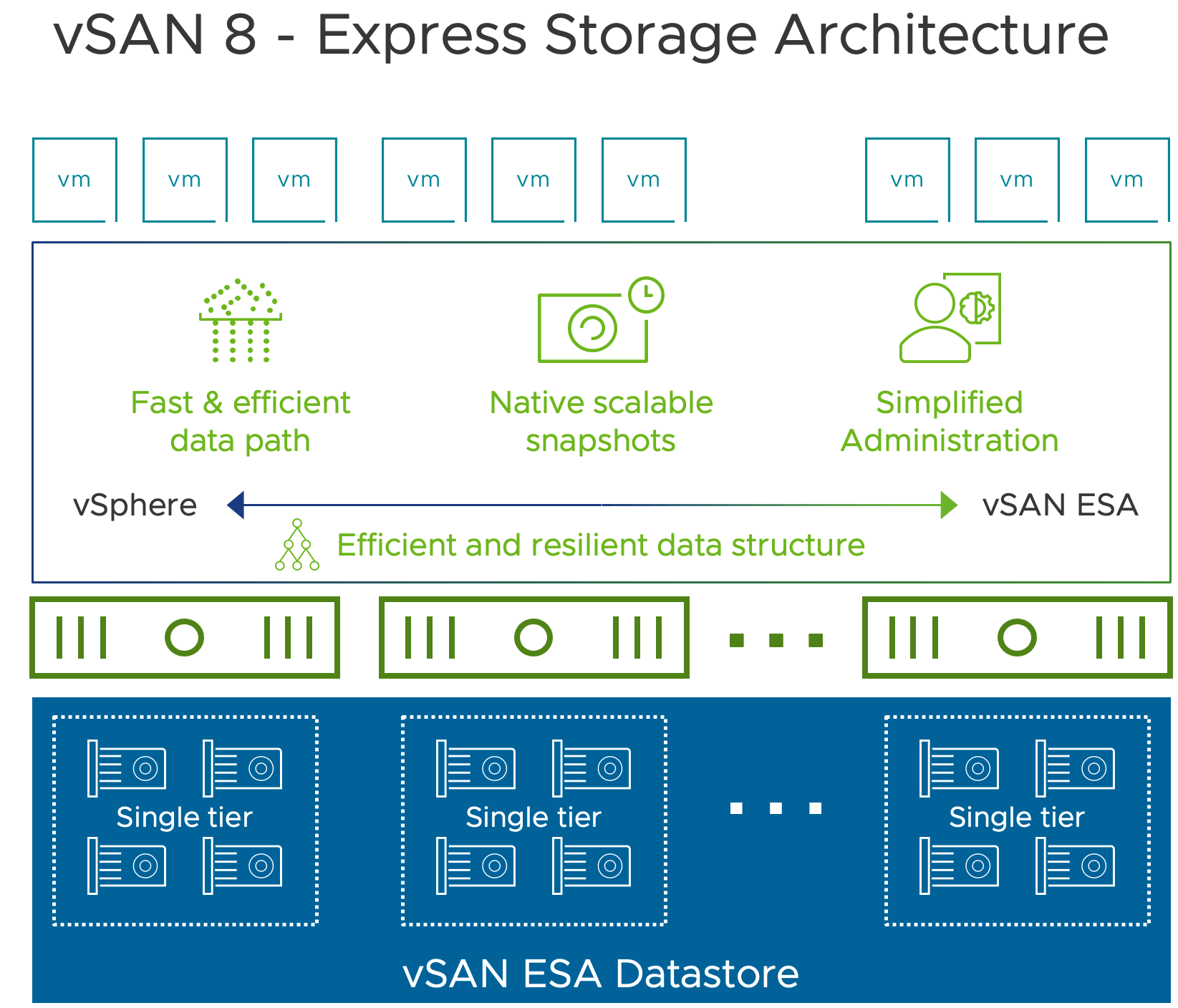
Key features and Enhancements in vSAN ESA
Each section explained below deserves its own blog, I will try to write about them one at a time in the coming days.. here are the key interesting features and enhancements of vSAN ESA
- vSAN ESA retains most of the key components part of the OSA’s architecture while adding new layers in between the existing vSAN layers. It introduces a new Log Structured File System (vSAN-LFS) which is patented. LFS helps to
- Ingest incoming write quickly with minimal overhead with help of Durable log, Metadata log and B-tree Caching, thus faster acknowledgement back to virtual machines when using an SPBM policy such as RAID-1, RAID-5 and RAID-6.
- Provide native vSAN-Snapshot feature, which provides consistent performance for VMs with snapshot and super fast (Consolidation/Deletion).
- Provides Compression by default to all vSAN objects which happens at the top of the stack, this reduces overall network bandwidth usage and IOPS to the storage devices and eliminates need of additional steps down the stack. This feature can be configured to be turned off on per object basis with use of Storage Policy Based Management (SPBM).
- Similar to Compression feature on ESA, checksum is enabled by default at top of the stack and is not configurable.
- Encryption also works in similar fashion as compression feature which is at the top of the stack and can be enabled/disabled globally (Both On-Disk and over Network),reduces CPU cost and I/O amplification.
- provide adaptive RAID-5 storage policy for objects at times when cluster size is down to just 3 nodes (OSA needs a minimum of 4 hosts),thus providing lower storage consumption (1.33x) vs RAID-1 (2x) per object.
- Existing Distributed Object Manager (DOM) is also enhanced to accomodate the new LFS layer, CPU performance optimizations, and also adds a new Network-Schedular which intelligently manages VM IO-traffic and resynchornization traffic using round trip latency poller in addition to overall bandwidth usage.
- Existing Log Structured Object Manager (LSOM) also had an overhaul on data structures and I/O Engine to provide extremely fast Single Tier performance (Yes! No more Disk Groups welcomes a Storage Pool concept), allowing all certified disks in a host to contribute to raw space, helps to claim devices automatically when new devices are added.
- Cluster Level Object Manager (CLOM) was also optimized for ESA to allows upto 27000 components per host which allows denser/more component placement vs OSA which had 9000 components per host limit. To work with the new LFS architecture, CLOM now creates a large CONCAT(concatenated) object at the top level and will have two break out legs underneath it called a Performance-Leg and a Capacity-Leg, where the performance leg accepts writes at the LFS layer and ack back to Guest, later this data from Performance-Leg is destaged back to Capacity legs.
- Cluster Monitoring, Membership, and Directory Services (CMMDS) and Reliable Datagram Transport (RDT) also had significant enhancements to reduce intra cluster traffic over the network using compression techniques and flow control
Conclusion
vSAN ESA is ideal HCI solution for all users who wants to get very low and reliable latency along with very high IO performance by exploiting latest new-gen hardware devices (CPU/Networking/Storage) to their fullest.
vSAN OSA which is still very good for many cases and will continue to co-exist with vSAN-ESA. This initial release of vSAN 8 doesnt support cluster conversion/upgrade from vSAN OSA to vSAN ESA, storage vMotion from OSA to ESA cluster is the only available option.
Please read official VMware blog here to know more about vSAN-ESA.